Author:Xiaoyang scallion circle
Author: 2077Research Source: X, @2077Research Translation: Shan Oppa,
in usRollups 2.0 SeriesIn our first article, we discussed Layer 1 (L1)-based rollups—the most decentralized and Ethereum-compatible way to manage rollups. By offloading the task of ordering transactions to Ethereum L1, L1-based rollups are able to take advantage of L1’s decentralization, simplicity, and liveness, while also bringing other benefits.
In today’s article, we’ll explore the next evolution of rollup:Booster Rollups. Booster Rollups is not only built on L1-based rollups, but also further expands the composability of Ethereum. But how do we actually extend this composability?
Current issues with L2 space
To ensure that the L2 network is functioning as expected, additional checks are often required. However, the main settlement and execution process still happens directly on L1. This means that while L2 extends functionality (such as off-chain EVM execution), it also adds additional complexity. While this additional logic is not ideal, the ultimate goal is to standardize operations and rely entirely on the standard EVM.
standardizationIt is crucial to achieve smooth transaction exchange between different L2s. To achieve this, a new type of transaction may be needed - one that can operate across multiple chains.
In this system, a transaction can generate smaller sub-transactions. Each sub-transaction contains the following details:
1. ID of the source chain
2. ID of the target chain
3. Enter data (e.g. caller, address and call data)
4. Output produced by the target chain
Two major functions of this transaction data:
1.as input on the source chain
It allows participants to view the output directly without directly involving the target chain.
2.Verify input and output consistency on the target chain
It is used to confirm whether the given input produces the expected output.
In this way, each chain can independently verify its own transactions while adhering to shared standards for transaction formats and inputs.
This approach keeps block verification simple, using familiar L1 verification contracts to ensure block validity. This shared standard and improved cross-chain transaction method lays a solid foundation for the future development of the L2 network and also makesBooster RollupsBecome the key to promoting the development of the Ethereum ecosystem.
How are Booster Rollups different?
Booster Rollups handle transactions similarly to executing on L1, they have access to L1's state but have independent storage, extending execution and storage to L2. Each L2 extends the block space of L1, spreading transaction processing and data storage over a wider area.
Imagine deploying a decentralized application (dapp) once and having it automatically scale to all Layer 2 (L2) networks. If you need more block space, just add more Booster Rollups, no additional configuration is required. This means no added effort, redeployment costs, or additional complexity for developers.
In simple terms, Booster Rollups are like adding more CPUs or SSDs to your laptop: they increase performance, allowing applications to run more efficiently while scaling easily.
from a technical perspective, Booster Rollups can also be described as “distributing transaction execution and storage across multiple shards”.
How Booster Rollups work
Whether it is optimistic rollup (Optimistic Rollup) or zero-knowledge rollup (ZK rollup), the Booster function can be used. However, not all rollups require Full Boosting, and some can benefit from L2-specific optimizations.
If the goal is to achieve native Ethereum scaling, the best improvement scenario is to implement it on L1-based Rollup. Scale Ethereum in a seamless way by letting L1 validators propose blocks for the entire Boosted network.
Boosted Rollups also solves the fragmentation problem prevalent in the current Rollup ecosystem. Through L1-based sequencing (Based Sequencing), they not only retain the advantages of L1 sequencing, but also introduce atomic cross-Rollup transactions within all L2 Booster networks. This design realizes the scaling vision envisioned for Ethereum from the beginning—to be both integrated and scalable, providing a unified solution to Ethereum’s growth challenges.
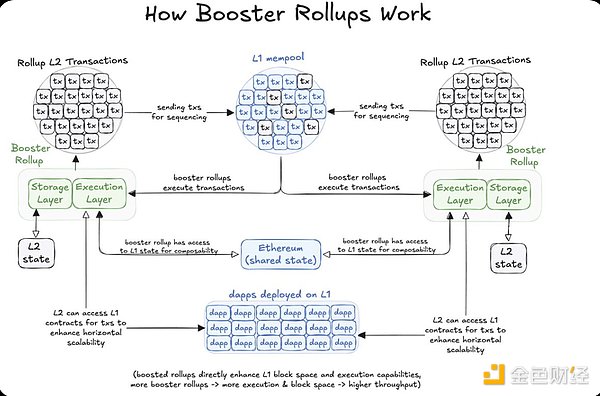
Because Booster Rollups naturally supports synchronous composability, this rollup model eliminates the hassle of dealing with fragmentation or switching between multiple L2s. All priority decentralized applications (dapps) are available on every L2, providing users with a seamless Ethereum experience.
Using Booster Rollups, developers can scale their dapps without having to redeploy multiple times across multiple L2s. Deploy once on L1 and dapps automatically scale to all existing and future Boosted L2s, greatly simplifying the development and deployment process.
Because Booster Rollups naturally supports synchronous composability, this rollup model eliminates the hassle of dealing with fragmentation or switching between multiple L2s. All priority decentralized applications (dapps) are available on every L2, providing users with a seamless Ethereum experience.
Using Booster Rollups, developers can scale their dapps without having to redeploy multiple times across multiple L2s. Deploy once on L1 and dapps automatically scale to all existing and future Boosted L2s, greatly simplifying the development and deployment process.
Advantages of Booster Rollups
1.Transparent scalability
Booster Rollups enhance scalability by transparently adding more servers to a server farm. Applications can seamlessly leverage additional resources, and developers can scale solutions without deploying complex L2 infrastructure.
2.Solve the problem of fragmentation
Booster Rollups provide a unified user experience between L1 and L2. Since smart contracts share the same address across all networks, users can enjoy consistency and simplicity in both L1 and L2 environments.
3.Solve the problem of low deployment efficiency
Developers only need to deploy once on L1, and dapps can support multiple Rollups by default, while updates are managed centrally. Whether users use an external account (EOA) or a smart wallet, they can conduct seamless transactions across the network through a single address.
4.Addressing Rollup Operator Attractiveness Issues
Developers do not need to specifically choose a deployment network, dapps will automatically support each Rollup network. Booster Rollups can be combined with L1-based Rollups to achieve significant scaling. Also, not all L2 needs to be Booster Rollups, making hybrid networks possible.
5.Increased sovereignty and security
Booster Rollups eliminate the need for specific wrapper contracts because smart contracts work the same way on L1 and L2, and control remains in the hands of the developer. By applying security measures to each dapp individually, rather than relying on bridges or specific implementations, security is significantly improved while eliminating the risk of a single point of failure.
About the limitations of Booster Rollups
To ensure that L2 can be consistent with L1, smart contract deployment should be limited to L1. This restriction ensures uniform access between L2s. This is not a significant limitation because smart contracts can still exhibit different behaviors through a data-driven approach, for example the contract address stored on the chain can change between different chains.
While L1 holds shared data, this does not directly improve scalability, a challenge inherent in any scalable system. Developers must optimize to minimize this effect. Similar to traditional software, not all decentralized applications (dapps) can fully take advantage of parallel processing. However, even if these dapps run on separate L2s, they can still benefit from interoperability because they remain universally accessible to all users.
Booster Rollups are essentially an extension of L1, but they have unique mechanisms for transaction execution and storage. In order to correctly interpret Booster Rollup transactions, L1 and L2 nodes must remain synchronized. One possible solution is to run both L1 and L2 on the same node, switching between shared L1 storage and L2 specific storage when executing transactions.
in conclusion
Booster Rollups provide a transformative solution to Ethereum's scaling challenges by improving transaction throughput and storage efficiency through seamless integration with L1. They solve problems such as fragmentation and deployment inefficiencies, allowing developers to easily scale dapps across multiple L2s while maintaining security and sovereignty.
By simplifying scalability and promoting interoperability, Booster Rollups paves the way for a more unified, user-friendly Ethereum ecosystem.















No Comments